Zambia has several laws and policies that aim to protect victims of Gender-Based Violence (GBV) and support survivors. These laws encompass various forms of GBV, including physical, sexual, emotional, psychological, and economic violence.

If you or someone you know is a victim of GBV, the following resources are available:
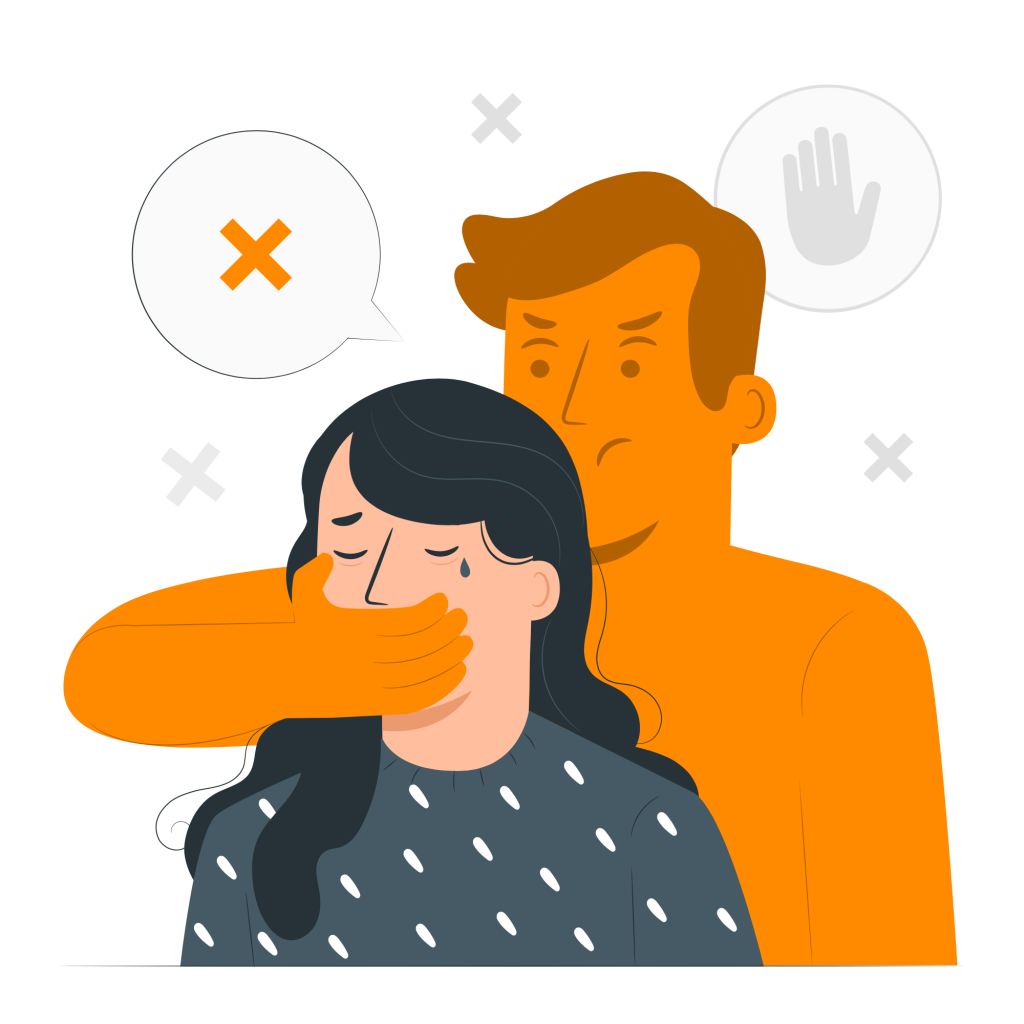


Gender-Based Violence refers to harmful acts directed at individuals based on their gender. This can include physical, sexual, emotional, psychological, and economic violence, as well as harassment and discrimination. GBV often disproportionately affects women, girls, and marginalized groups.
The main types of GBV include:
GBV can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background, though it predominantly affects women, girls, and marginalized communities. However, men, boys, and gender-diverse individuals can also be victims of GBV.
Warning signs of GBV can include:
If you or someone you know is experiencing GBV, consider:
There are so many shelters or safe spaces where survivors of GBV can find temporary housing, protection, and support around Zambia with the help of GBV based organisation. Our Knowledge Center includes a list of verified safe spaces and emergency contact information.
Experiencing GBV can lead to a range of mental health challenges, including depression, anxiety, PTSD, low self-esteem, and difficulty in trusting others. Survivors often need mental health support, counseling, and community resources to begin healing.
Yes, many NGO’s have capacity and laws protecting individuals from GBV and offer legal support, including restraining orders, legal representation, and assistance with filing reports. Contact local authorities or a legal aid organization to understand your rights.
Yes, men and boys can experience GBV, although it may be less reported due to stigma or cultural beliefs. Male survivors can access the same support and resources available to women, including counseling, legal aid, and shelter options.
If someone you know is experiencing GBV, you can:

Reporting GBV varies by location, but generally, you can:
While it is never a victim’s fault, there are steps that can enhance personal safety:
GBV stems from power imbalances, societal norms, cultural beliefs, and a lack of accountability. Preventing GBV requires community education, legal action, support services, and challenging harmful gender stereotypes.
