Zambia has several laws and policies that aim to protect victims of Gender-Based Violence (GBV) and support survivors. These laws encompass various forms of GBV, including physical, sexual, emotional, psychological, and economic violence.

Mental health encompasses our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act, as well as how we handle stress, relate to others, and make choices. Good mental health is essential for overall well-being and can influence physical health, relationships, and productivity.
Common mental health disorders include:
Recognizing mental health issues can be challenging. Common signs include persistent sadness, excessive worrying, changes in mood or behavior, withdrawal from social activities, difficulty concentrating, and changes in sleeping or eating habits. If these symptoms persist for more than two weeks and interfere with daily life, consider reaching out to a mental health professional.
Mental health refers to the state of our emotional and psychological well-being, which can fluctuate throughout life. Mental illness, however, refers to diagnosed disorders that affect mood, thinking, and behavior. While everyone has mental health, not everyone experiences mental illness.
Yes, mental health issues are prevalent worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), one in four people will be affected by a mental disorder at some point in their lives. Recognizing the commonality of these issues helps reduce stigma and encourages seeking help.

Treatments vary based on the condition and individual needs but may include:
The main types of GBV include:
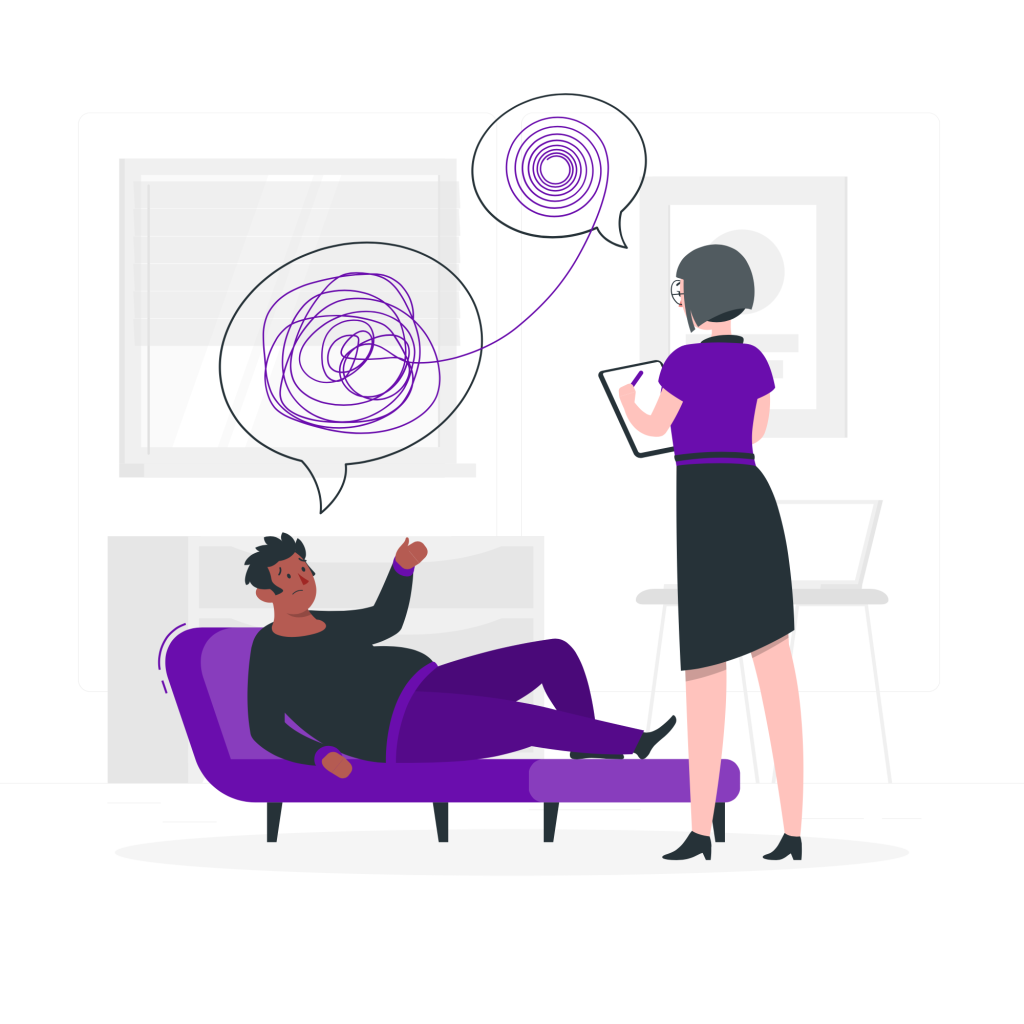
The first session typically involves discussing your history, current challenges, and what you hope to achieve through therapy. The therapist may ask questions to understand your situation better and assess your needs. It’s also an opportunity for you to ask questions about their approach and establish rapport.
Offer your listening ear without judgment, validate their feelings, and encourage them to seek professional help. Educate yourself about their condition to understand their experience better. Be patient and remind them that seeking help is a sign of strength.
A mental health crisis occurs when someone’s emotional state deteriorates to a point where they are unable to cope or function safely. If you or someone else is in immediate danger, call emergency services. For non-emergency situations, contact a mental health crisis hotline or encourage the individual to reach out to a professional.
Self-care can help manage stress and enhance emotional well-being. Effective strategies include:
Identify triggers and use coping techniques such as:
Physical activity has been shown to release endorphins, which improve mood and reduce feelings of anxiety and depression. Regular exercise can also enhance self-esteem, provide a sense of achievement, and serve as a healthy outlet for stress.
Sleep is crucial for emotional regulation and cognitive functioning. Lack of sleep can exacerbate mental health issues, leading to increased stress, anxiety, and depression. Establish a regular sleep routine and create a restful environment to improve sleep quality.


If you are in immediate danger, call emergency services or a suicide prevention hotline. It’s vital to talk to someone who can help, whether a trusted friend, family member, or mental health professional. You are not alone, and help is available.
Yes, many organizations and platforms offer virtual support groups. Look for reputable websites that provide safe, moderated spaces for individuals to share experiences and support one another, often based on specific conditions or topics.
Mental health and physical health are interconnected. Poor mental health can lead to physical issues such as chronic pain, fatigue, and a weakened immune system. Conversely, physical health problems can contribute to mental health struggles. Taking care of both aspects is crucial for overall well-being.
Mental health stigma involves negative stereotypes and misconceptions that contribute to discrimination against those with mental health issues. Reducing stigma requires education, open dialogue, and shared personal experiences to foster understanding and compassion.
Consider joining local or national mental health organizations, participating in awareness campaigns, volunteering, or sharing your story to reduce stigma. Advocacy can also include educating others about mental health and encouraging community discussions.
